
#LOOP IN R HOW TO#
The following code illustrates how to write and use while-loops in R. This code is typically used when we don’t know the exact number of times our R code needs to be executed. While-loops repeat a code block as long as a certain logical condition is TRUE. Now, you could make the body of this for loop more complex to create more advanced outputs.Ĭlick here to find more detailed explanations and advanced programming examples of for-loops in R. the values 1 to 10).Īt this point, you basically know how to write and run a for-loop in the R programming language. The RStudio console output is showing the final outputs of our for-loop (i.e. Note that we have to use the print function to visibly return values within a for-loop. x_for + 1) and prints the updated data object to the RStudio console using the print function (i.e. The body of our for-loop adds +1 to our data object (i.e.

For loops in R always iterate over a sequence (a vector), where the length of the vector. Also note that running indices can not be changed by the user within for-loops. The simplest and most frequently used type of loops is the for loop. Note that our running index i is increased by 1 within each iteration. i) and the collection of objects through which we want to iterate (i.e. The head of our for-loop defines the running index (i.e. elements in a vector or list) to which a code block should be applied.Ī for-loop consists of two parts: First, a header that specifies the collection of objects Second, a body containing a code block that is executed once per object.įirst, we have to specify a data object that we can use within the for-loop: Loops are iterative structures which repeat a statement or a block of code - a sequence of instructions depending on certain conditions. In this article you will learn how to create a for loop in R programming with examples & exercises for practice. So keep on reading!įor-loops specify a collection of objects (e.g. A for loop is used to repeat a block of code. In this structure, the RNA is base-paired to one of the.
#LOOP IN R PLUS#
There is only one difference between for and while, i.e., in while loop, the condition is checked before the execution of the body, but in for loop condition is checked after the execution of the body. An R-loop is a nucleic acid structure consisting of two antiparallel DNA strands plus one RNA strand.

In the following, I’ll explain the different types of loops and illustrate the differences in R programming example codes. A for loop is the most popular control flow statement. Today, we will take a look at these control structures that R provides and learn how to use them. There are also looping structures that loop or repeat code sections based on certain conditions and state. In R, there are decision-making structures like if-else that control execution of the program conditionally. The following graphic is illustrating the workflow of each of the three loop-types: There are a few control structures in R that help control the flow of the program. The R programming language generally provides three different types of loops: for-loops, while-loops, and repeat-loops. The loop executes a code block again and again until no further action is required.Įach time the code block within the loop is executed is called an iteration.ĭepending on your specific programming situation, you may need different loop-structures that execute the code blocks within the loop on the basis of different conditions.
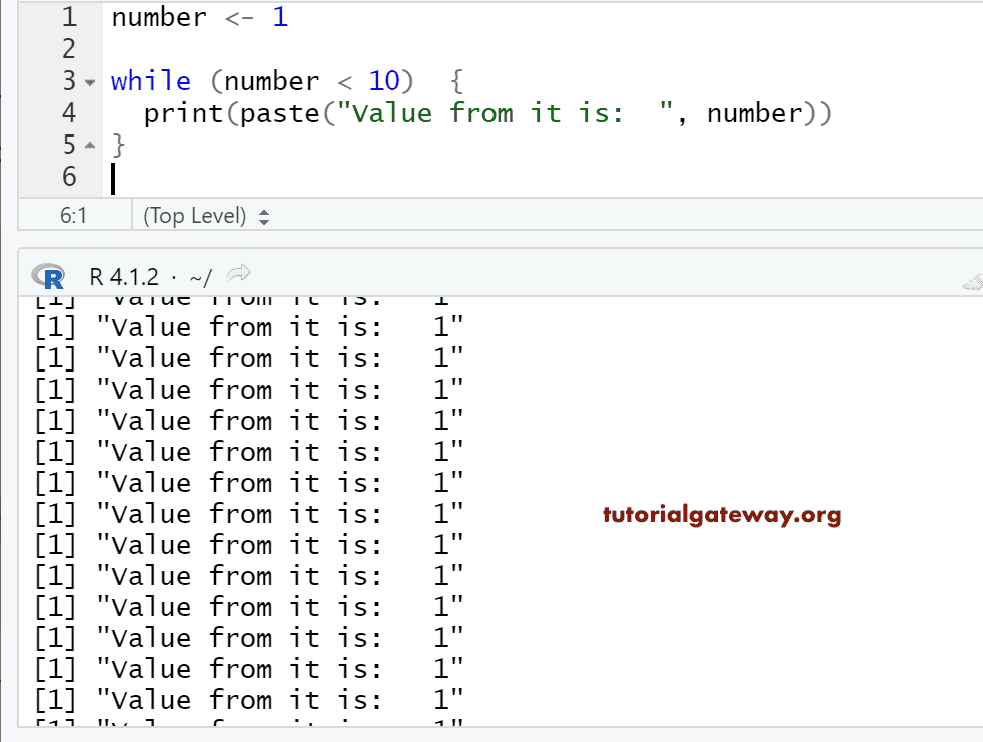
While loops are used when you don't know the exact number of times a block of code is to be repeated.6) Advanced Tutorials on Loops What are Loops? Ī loop is a programming instruction that repeats until a specific condition is reached. Loops help you to save time, avoid repeatable blocks of code, and write cleaner code. In programming, loops are used to repeat a block of code as long as the specified condition is satisfied.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
